The research team from the Max Planck Institute for Iron Research in Germany is at the forefront of this technology1. They use an electric arc furnace to melt red mud and expose it to a plasma of ionized hydrogen atoms3. In just about 10 minutes, iron oxide is reduced by the plasma to form liquid iron, which is then easily separated from the slag based on density differences. The obtained iron is of high purity and can be directly used for steel - making, which greatly simplifies the steel - making process.
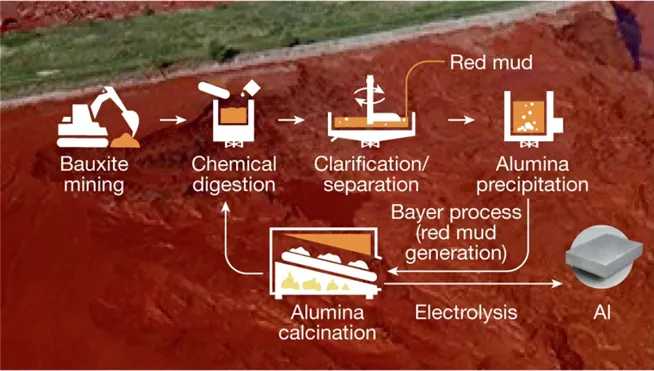
This technology not only has high - efficiency in iron extraction but also significant environmental benefits7. Red mud, as a by - product of bauxite refining into alumina, has become one of the most environmentally harmful industrial wastes4. The new method can convert this waste into valuable iron, while the remaining substances have a pH value close to neutral and can be used in building materials, achieving resource recycling. Moreover, when using green hydrogen and renewable energy, the carbon footprint of the entire process is extremely low, which is in line with the global trend of carbon neutrality.
In the future, with the continuous improvement of this technology, it is expected to be widely applied in the metal smelting industry, providing a new idea for solving the problem of industrial waste treatment and promoting the sustainable development of the metallurgical industry.